A new economics study is pushing back on the idea that artificial intelligence will mainly widen inequality by rewarding only highly skilled workers.
In a recent paper, researchers from Stanford University and CREi analyzed how generative AI affects work at the task level and found that AI could raise average wages, while reducing wage inequality across the labor market.
Rather than focusing on whether AI replaces jobs outright, the study examines how AI changes what workers actually do inside their jobs. The researchers model how AI affects individual tasks, how those changes alter worker productivity and how wages adjust across the economy.
The analysis draws on decades of US labor market data, detailed task descriptions from O*NET, and wage histories from the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth. The model is then used to simulate what happens when generative AI is introduced at scale.
The researchers identify three ways AI affects work: it can automate some tasks, speed up others and simplify tasks by lowering the skill required to perform them.
Using task-level estimates, the study finds that generative AI reduces required skill levels by an average of about 18% across tasks. In many cases, tasks drop by roughly one level on standard job skill scales, particularly in writing, planning, judgment and decision-making.
When AI is added to the model, average wages rise by roughly 21%. Most of the overall wage increase comes from productivity gains, allowing workers to complete tasks more efficiently with AI assistance.
“Average wages, in contrast, rise mainly due to augmentation, with automation and simplification having smaller effects on average.”
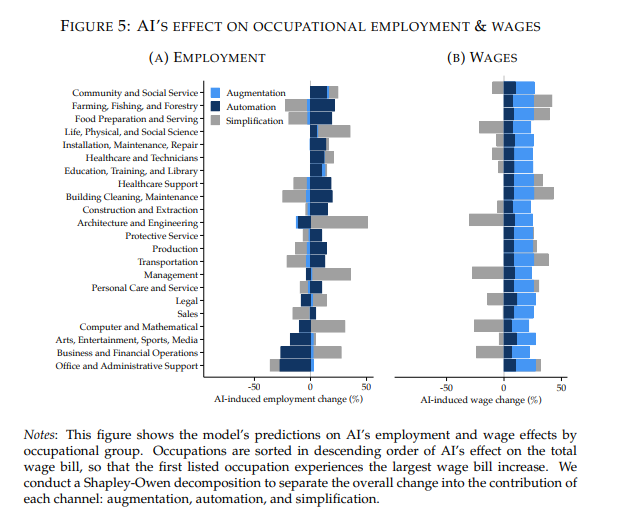
However, the reduction in wage inequality comes from a different channel.
By lowering the skill barriers inside jobs, task simplification allows more workers to compete for roles that were previously limited to higher-skilled workers. That expanded competition compresses wage differences across workers.
To isolate the effect, the researchers test each AI channel separately. Automation alone does not significantly change inequality. Productivity gains alone also fail to narrow wage gaps. Only task simplification produces the equalizing effect.
“Simplification lowers inequality in two ways. First, it reduces wage dispersion within occupations by enabling lower-skilled workers to perform tasks more productively. Second, it reduces wage differences across occupations by making occupations with high skill requirements more accessible to less skilled workers, reducing its relative price.”
Lower-skill workers see the largest percentage gains, particularly those with weaker verbal skills, where AI tools are most effective. Math-intensive skills retain more of their wage premium, as AI simplifies those tasks less.
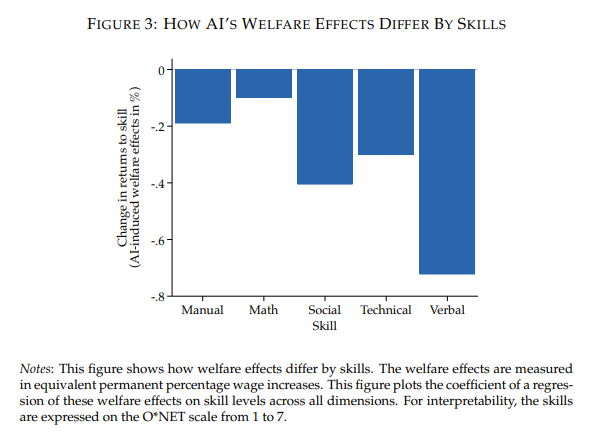
Taken together, the findings suggest AI’s most significant labor market effect may not be job replacement, but the quiet lowering of skill barriers that once separated higher-paying work from the rest of the workforce.
Disclaimer: Opinions expressed at CapitalAI Daily are not investment advice. Investors should do their own due diligence before making any decisions involving securities, cryptocurrencies, or digital assets. Your transfers and trades are at your own risk, and any losses you may incur are your responsibility. CapitalAI Daily does not recommend the buying or selling of any assets, nor is CapitalAI Daily an investment advisor. See our Editorial Standards and Terms of Use.


